Location
Bldg 1050 Suite B
Wichita, Kansas 67205
Hours
8am – 5pm

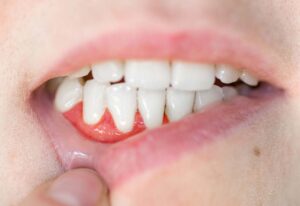

Gum recession happens when gum tissue that surrounds the teeth wears away and exposes more of the tooth. In some cases, receding gums can lead to exposure of the tooth’s root. As a result, gaps can form between the teeth and gum line which creates a space for bacteria to harbor.
If left untreated, the tissue, tooth, and bone can sustain serious damage which can lead to disease and tooth loss.
Gum recession is a fairly common dental problem—most people are unaware they have receding gums because it occurs over time.
While gum tissue does not grow back, there are professional treatment options and preventative steps you can take. Mild gum recession can be treated by your dentist with a thorough exam and deep clean. During this appointment, your dentist will remove plaque and tartar buildup on your teeth.
In more serious cases, surgery for your recession may be necessary. This treatment can include bone regeneration, tissue graft, or gum graft to address the issue.
The best way to prevent receding gums is to visit your dentist twice yearly for routine exams and cleanings. At your appointment, your dentist can easily identify early signs of gum disease. In addition, exercising smart oral health habits can prevent gum problems from developing.
If you notice signs of your gums receeding, you should act quickly to address the problem. Contact your dental office for an immediate appointment to prevent further damage from spreading.